Nikola Tesla

Introduction
Inventor Nikola Tesla was born in July of 1856, in what is now Croatia. He came to the United States in 1884 and briefly worked with Thomas Edison before the two parted ways. He sold several patent rights, including those to his alternating-current machinery, to George Westinghouse. His 1891 invention, the "Tesla coil," is still used in radio technology today. Tesla died in New York City on January 7, 1943.
Early Years
Nikola Tesla was born on July 10, 1856, in what is now Smiljan, Croatia. He was one of five children which included siblings Dane, Angelina, Milka and Marica, in the family. Tesla's interest in electrical invention was spurred by his mother, Djuka Mandic, who invented small household appliances in her spare time while her son was growing up. Tesla's father, Milutin Tesla, was a Serbian orthodox priest and a writer, and he pushed for his son to join the priesthood. But Nikola's interests lay squarely in the sciences. After studying at the Realschule, Karlstadt (later renamed the Johann-Rudolph-Glauber Realschule Karlstadt); the Polytechnic Institute in Graz, Austria; and the University of Prague during the 1870s, Tesla moved to Budapest, where for a time he worked at the Central Telephone Exchange. It was while in Budapest that the idea for the induction motor first came to Tesla, but after several years of trying to gain interest in his invention, at age 28 Tesla decided to leave Europe for America.
Famed Inventor
In 1884 Tesla arrived the United States with little more than the clothes on his back and a letter of introduction to famed inventor and business mogul Thomas Edison, whose DC-based electrical works were fast becoming the standard in the country. Edison hired Tesla, and the two men were soon working tirelessly alongside each other, making improvements to Edison's inventions. However, several months later, the two parted ways due to a conflicting business-scientific relationship.
After parting ways with Edison, in 1885 Tesla received funding for the Tesla Electric Light Company and was tasked by his investors to develop improved arc lighting. After successfully doing so, however, Tesla was forced out of the venture and for a time had to work as a manual laborer in order to survive. His luck changed in 1887, when he was able to find interest in his AC electrical system and funding for his new Tesla Electric Company. Setting straight to work, by the end of the year, Tesla had successfully filed several patents for AC-based inventions.
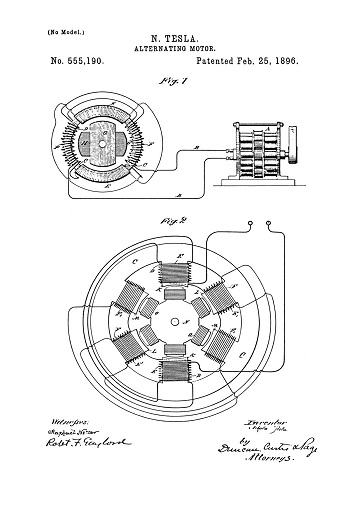
Tesla's AC system eventually caught the attention of American engineer and business man George Westinghouse, who was seeking a solution to supplying the nation with long-distance power. Convinced that Tesla's inventions would help him achieve this, in 1888 he purchased his patents for $60,000 in cash and stock in the Westinghouse Corporation. As interest in an alternating-current system grew, Tesla and Westinghouse were put in direct competition with Thomas Edison, who was intent on selling his direct-current system to the nation. A negative-press campaign was soon waged by Edison, in an attempt to undermine interest in AC power. Tesla, for his part, continued in his work and would patent several more inventions during this period, including the "Tesla coil," which laid the foundation for wireless technologies and is still used in radio technology today.
Unfortunately for Thomas Edison, the Westinghouse Corporation was chosen to supply the lighting at the 1893 World's Columbian Exposition in Chicago, and Tesla conducted demonstrations of his AC system there. Two years later, in 1895, Tesla designed what was among the first AC hydroelectric power plants in the United States, at Niagara Falls. The following year, it was used to power the city of Buffalo, New York, a feat that was highly publicized throughout the world. With its repeat successes and favorable press, the alternating-current system would quickly become the preeminent power system of the 20th century, and it has remained the worldwide standard ever since.
In addition to his AC system and coil, throughout his career, Tesla discovered, designed and developed ideas for a number of other important inventions—most of which were officially patented by other inventors—including dynamos (electrical generators similar to batteries) and the induction motor. He was also a pioneer in the discovery of radar technology, X-ray technology, remote control and the rotating magnetic field—the basis of most AC machinery.
" Let the future tell the truth, and evaluate each one according to his work and accomplishments. The present is theirs; the future, for which I have really worked, is mine. "
Fall from Grace
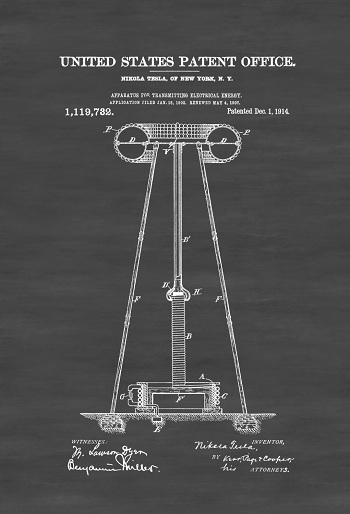
Having become obsessed with the wireless transmission of energy, around 1900 Nikola set to work on his boldest project yet: to build a global, wireless communication system—to be transmitted through a large electrical tower—for sharing information and providing free electricity throughout the world. With funding from a group of investors that included financial giant J. P. Morgan, in 1901 Tesla began work on the project in earnest, designing and building a lab with a power plant and a massive transmission tower on a site on Long Island, New York, that became known as Wardenclyffe. However, when doubts arose among his investors about the plausibility of Tesla's system and his rival, Guglielmo Marconi—with the financial support of Andrew Carnegie and Thomas Edison—continued to make great advances with his own radio technologies, Tesla had no choice but to abandon the project. The Wardenclyffe staff was laid off in 1906 and by 1915 the site had fallen into foreclosure. Two years later Tesla declared bankruptcy and the tower was dismantled and sold for scrap to help pay the debts he had accrued.
"The scientists of today think deeply instead of clearly. One must be sane to think clearly, but one can think deeply and be quite insane. "
Death
After suffering a nervous breakdown, Tesla eventually returned to work, primarily as a consultant. But as time went on, his ideas became progressively more outlandish and impractical. He also grew increasingly eccentric, devoting much of his time to the care of wild pigeons in New York City's parks. He even drew the attention of the FBI with his talk of building a powerful "death beam," which had received some interest from the Soviet Union during World World II. Poor and reclusive, Nikola Tesla died on January 7, 1943, at the age of 86, in New York City, where he had lived for nearly 60 years.
"Our virtues and our failings are inseparable, like froce and matter. When they separate, man is no more."
Inventions
| Inventions | Description |
|---|---|
| Alternating current | Tesla introduced his motors and electrical systems in a classic paper, “A New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers” which he delivered before the American Institute of Electrical Engineers in 1888. One of the most impressed was the industrialist and inventor George Westinghouse. One day he visited Tesla’s laboratory aTesla Statuend was amazed at what he saw. Tesla had constructed a model polyphase system consisting of an alternating current dynamo, step-up and step-down transformers and A.C. motor at the other end. The perfect partnership between Tesla and Westinghouse for the nationwide use of electricity in America had begun. |
| Light | He invented how light can be harnessed and distributed. Tesla developed and used fluorescent bulbs in his lab some 40 years before industry “invented” them. At the World’s Fair, Tesla took glass tubes and bent them into famous scientists’ names, in effect creating the first neon signs. However, it is his Tesla Coil that might be the most impressive, and controversial. The Tesla Coil is certainly something that big industry would have liked to suppress: the concept that the Earth itself is a magnet that can generate electricity (electromagnetism) utilizing frequencies as a transmitter. All that is needed on the other end is the receiver — much like a radio. |
| X-rays | Electromagnetic and ionizing radiation was heavily researched in the late 1800s, but Nikola Tesla researched the entire gamut. Everything from a precursor to Kirlian photography, which has the ability to document life force, to what we now use in medical diagnostics, this was a transformative invention of which Tesla played a central role. X-rays, like so many of Tesla's contributions, stemmed from his belief that everything we need to understand the universe is virtually around us at all times, but we need to use our minds to develop real-world devices to augment our innate perception of existence. |
| Radio | Guglielmo Marconi was initially credited, and most believe him to be the inventor of radio to this day. However, the Supreme Court overturned Marconi’s patent in 1943, when it was proven that Tesla invented the radio years previous to Marconi. Radio signals are just another frequency that needs a transmitter and receiver, which Tesla also demonstrated in 1893 during a presentation before The National Electric Light Association. In 1897 Tesla applied for two patents US 645576, and US 649621. In 1904, however, The U.S. Patent Office reversed its decision, awarding Marconi a patent for the invention of radio, possibly influenced by Marconi’s financial backers in the States, who included Thomas Edison and Andrew Carnegie. This also allowed the U.S. government (among others) to avoid having to pay the royalties that were being claimed by Nikola Tesla. |
| Remote Control | This invention was a natural outcropping of radio. Patent No. 613809 was the first remote controlled model boat, demonstrated in 1898. Utilizing several large batteries; radio signals controlled switches, which then energized the boat’s propeller, rudder, and scaled-down running lights. While this exact technology was not widely used for some time, we now can see the power that was appropriated by the military in its pursuit of remote controlled war. Radio controlled tanks were introduced by the Germans in WWII, and developments in this realm have since slid quickly away from the direction of human freedom. |
| Electric Motor | Nikola Tesla’s invention of the electric motor has finally been popularized by a car brandishing his name. While the technical specifications are beyond the scope of this summary, suffice to say that Tesla’s invention of a motor with rotating magnetic fields could have freed mankind much sooner from the stranglehold of Big Oil. However, his invention in 1930 succumbed to the economic crisis and the world war that followed. Nevertheless, this invention has fundamentally changed the landscape of what we now take for granted: industrial fans, household applicances, water pumps, machine tools, power tools, disk drives, electric wristwatches and compressors. |
| Robotics | Nikola Tesla’s overly enhanced scientific mind led him to the idea that all living beings are merely driven by external impulses. He stated: “I have by every thought and act of mine, demonstrated, and does so daily, to my absolute satisfaction that I am an automaton endowed with power of movement, which merely responds to external stimuli.” Thus, the concept of the robot was born. However, an element of the human remained present, as Tesla asserted that these human replicas should have limitations — namely growth and propagation. Nevertheless, Nikola Tesla unabashedly embraced all of what intelligence could produce. |
| Laser | Nikola Tesla’s invention of the laser may be one of the best examples of the good and evil bound up together within the mind of man. Lasers have transformed surgical applications in an undeniably beneficial way, and they have given rise to much of our current digital media. However, with this leap in innovation we have also crossed into the land of science fiction. From Reagan’s “Star Wars” laser defense system to today’s Orwellian “non-lethal” weapons’ arsenal, which includes laser rifles and directed energy “death rays,” there is great potential for development in both directions. |
| Wireless Communications and Limitless Free Energy | These two are inextricably linked, as they were the last straw for the power elite — what good is energy if it can’t be metered and controlled? Free? Never. J.P. Morgan backed Nikola Tesla with $150,000 to build a tower that would use the natural frequencies of our universe to transmit data, including a wide range of information communicated through images, voice messages, and text. This represented the world’s first wireless communications, but it also meant that aside from the cost of the tower itself, the universe was filled with free energy that could be utilized to form a world wide web connecting all people in all places, as well as allow people to harness the free energy around them. Essentially, the 0’s and 1’s of the universe are embedded in the fabric of existence for each of us to access as needed. Nikola Tesla was dedicated to empowering the individual to receive and transmit this data virtually free of charge. |
 Four Interesting People
Four Interesting People