Ada Lovelace

Introduction
Augusta Ada King-Noel, Countess of Lovelace (née Byron; 10 December 1815 – 27 November 1852) was an English mathematician and writer, chiefly known for her work on Charles Babbage's early mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine. Her notes on the engine include what is recognized as the first algorithm intended to be carried out by a machine. As a result, she is often regarded as the first computer programmer.
The First computer program
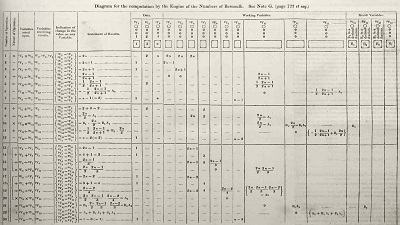
In 1840, Babbage was invited to give a seminar at the University of Turin about his Analytical Engine. Luigi Menabrea, a young Italian engineer, and the future Prime Minister of Italy, wrote up Babbage's lecture in French, and this transcript was subsequently published in the Bibliothèque universelle de Genève in October 1842. Babbage's friend Charles Wheatstone commissioned Ada Lovelace to translate Menabrea's paper into English. She then augmented the paper with notes, which were added to the translation. Ada Lovelace spent the better part of a year doing this, assisted with input from Babbage. These notes, which are more extensive than Menabrea's paper, were then published in Taylor's Scientific Memoirs under the initialism AAL.
In 1953, more than a century after her death, Ada Lovelace's notes on Babbage's Analytical Engine were republished. The engine has now been recognised as an early model for a computer and her notes as a description of a computer and software.
Ada Lovelace's notes were labelled alphabetically from A to G. In note G, she describes an algorithm for the Analytical Engine to compute Bernoulli numbers. It is considered the first published algorithm ever specifically tailored for implementation on a computer, and Ada Lovelace has often been cited as the first computer programmer for this reason. The engine was never completed so her program was never tested.
Beyond Numbers
In her notes, Lovelace emphasised the difference between the Analytical Engine and previous calculating machines, particularly its ability to be programmed to solve problems of any complexity. She realised the potential of the device extended far beyond mere number crunching. In her notes, she wrote:
"[The Analytical Engine] might act upon other things besides number, were objects found whose mutual fundamental relations could be expressed by those of the abstract science of operations, and which should be also susceptible of adaptations to the action of the operating notation and mechanism of the engine...Supposing, for instance, that the fundamental relations of pitched sounds in the science of harmony and of musical composition were susceptible of such expression and adaptations, the engine might compose elaborate and scientific pieces of music of any degree of complexity or extent."
This analysis was an important development from previous ideas about the capabilities of computing devices, and anticipated the implications of modern computing one hundred years before they were realised. Walter Isaacson ascribes Lovelace's insight regarding the application of computing to any process based on logical symbols to an observation about textiles: "When she saw some mechanical looms that used punchcards to direct the weaving of beautiful patterns, it reminded her of how Babbage's engine used punched cards to make calculations." This insight is seen as significant by writers such as Betty Toole and Benjamin Woolley, as well as the programmer John Graham-Cumming, whose project Plan 28 has the aim of constructing the first complete Analytical Engine.
In popular culture
| Year | Title | Author | Genre |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1977 | Childe Byron | Romulus Linney | Play |
| 1990 | The Difference Engine | William Gibson & Bruce Sterling | Novel |
| 1993 | Arcadia | Tom Stoppard | Play |
| 1997 | Conceiving Ada | Lynn Hershman Leeson | Film |
| 2005 | Lord Byron's Novel: The Evening Land | John Crowley | Novel |
| 2015 | Ada and the Memory Engine | Lauren Gunderson | Play |
Titles and Styles
- 10 December 1815 – 8 July 1835: The Honourable Ada Byron
- 8 July 1835 – 30 June 1838: The Right Honourable The Lady King
- 30 June 1838 – 27 November 1852: The Right Honourable The Countess of Lovelace
Controversy over the extent of contributions
Though Lovelace is referred to as the first computer programmer, some biographers and historians of computing claim the contrary. Allan G. Bromley, in the 1990 article Difference and Analytical Engines:
All but one of the programs cited in her notes had been prepared by Babbage from three to seven years earlier. The exception was prepared by Babbage for her, although she did detect a 'bug' in it. Not only is there no evidence that Ada ever prepared a program for the Analytical Engine, but her correspondence with Babbage shows that she did not have the knowledge to do so.
Bruce Collier, who later wrote a biography of Babbage, wrote in his 1970 Harvard University PhD thesis that Lovelace "made a considerable contribution to publicizing the Analytical Engine, but there is no evidence that she advanced the design or theory of it in any way."
Eugene Eric Kim and Betty Alexandra Toole consider it "incorrect" to regard Lovelace as the first computer programmer, as Babbage wrote the initial programs for his Analytical Engine, although the majority were never published. Bromley notes several dozen sample programs prepared by Babbage between 1837 and 1840, all substantially predating Lovelace's notes. Dorothy K. Stein regards Lovelace's notes as "more a reflection of the mathematical uncertainty of the author, the political purposes of the inventor, and, above all, of the social and cultural context in which it was written, than a blueprint for a scientific development."
 Four Interesting People
Four Interesting People